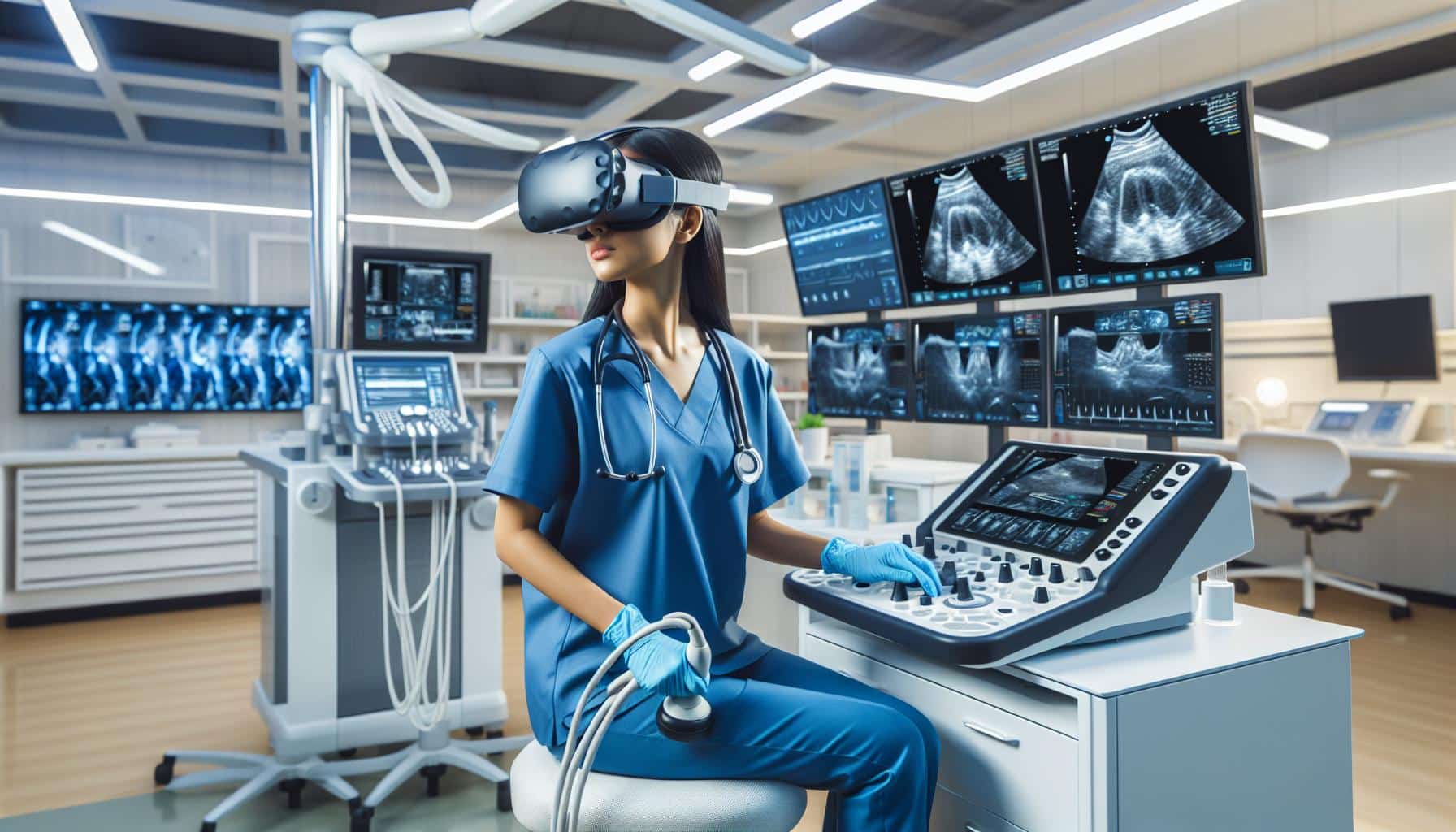
An Immersive VR-Based Test for Thoracic Ultrasound Skills
An immersive virtual reality (VR)-based test has been developed to assess the thoracic ultrasound skills of clinicians at different skill levels, according to a recent Danish study. Led by Anders Nielsen from Odense University Hospital in Svendborg, the research aimed to provide a standardized and evidence-based approach to evaluating operator competency in thoracic ultrasound. The test was based on the European Respiratory Society’s (ERS) protocol on thoracic ultrasound and involved the use of an immersive VR platform developed by VitaSim. The platform provided clinicians with various scenarios and zones for examination and diagnosis.
Experts Outperform Novice Users in VR-Based Ultrasound Test
The study found that there were significant differences in test scores between novice, intermediate, and expert ultrasound users. Expert users achieved the highest scores, while novice users scored the lowest. The findings suggest that experience and proficiency in thoracic ultrasound correlate with higher test performance. The test consisted of two clinical cases, and the results demonstrated that the expert users consistently outperformed both the intermediate and novice users across both cases. This indicates that experts possess a greater level of knowledge and skill in interpreting thoracic ultrasound images.
Objective Assessment of Operator Skills in Thoracic Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a user-dependent imaging modality, and operator skills are crucial for accurate diagnosis. The immersive VR-based test offers an objective and standardized method for assessing operator skills in thoracic ultrasound. The researchers used a scoring system where clinicians received one point for each correct response to test questions. The test demonstrated high consistency, with a Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.86 for the entire assessment. The results provide evidence that the test is a reliable tool for evaluating and comparing the proficiency of ultrasound operators.
Immersive VR Shows Promise in Advancing Medical Education
The use of immersive VR in medical education has shown promise, and this study adds to the growing body of research on its effectiveness. Immersive VR provides a realistic and interactive learning environment that can enhance hands-on medical education, including radiology training. Previous studies have highlighted the potential of VR in improving skills acquisition, knowledge retention, and diagnostic accuracy. By leveraging VR technology, medical educators can provide trainees with a more engaging and immersive learning experience.
Future Implications of Immersive VR in Ultrasound Education
The findings of this study open up possibilities for further research and development of immersive VR in ultrasound education. The authors suggest that future studies could explore a wide range of educational tools that are structured and evidence-based. This would allow institutions and participants to select the most suitable and efficient educational tool for their specific needs. Furthermore, the standardized portable test developed in this study could be incorporated into a simulation-based mastery learning program. This would ensure that clinicians receive comprehensive and standardized training in thoracic ultrasound, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
The use of immersive VR in medical education holds great potential for enhancing the skills and knowledge of healthcare professionals. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that VR will play an increasingly important role in medical training and education. With its ability to provide realistic simulations and objective assessments, immersive VR has the potential to revolutionize the way ultrasound skills are taught and evaluated.
Analyst comment
Positive news: The development of an immersive VR-based test for assessing thoracic ultrasound skills has been found to be effective in evaluating operator competency.
Market analysis: The adoption of immersive VR technology in medical education is expected to increase, as it has shown promise in enhancing skills acquisition and knowledge retention. This will likely lead to greater demand for VR-based educational tools and training programs in the healthcare industry.