Rebuilding Social Infrastructure: How Should We Invest in Communities?
Investing in public spaces is crucial to solving major issues like loneliness, mental health problems, and the public's lack of political interest. Such investments also have economic benefits by helping to balance the wealth differences between poorer and richer areas.
The Infrastructure Funding Gap
Globally, there is a massive gap in the funding needed for infrastructure, expected to exceed $15 trillion by 2040. In the UK, the National Infrastructure Commission reports that investment will need to increase by £15-25 billion annually by the 2030s to meet growing demands.
Importance of Social Infrastructure
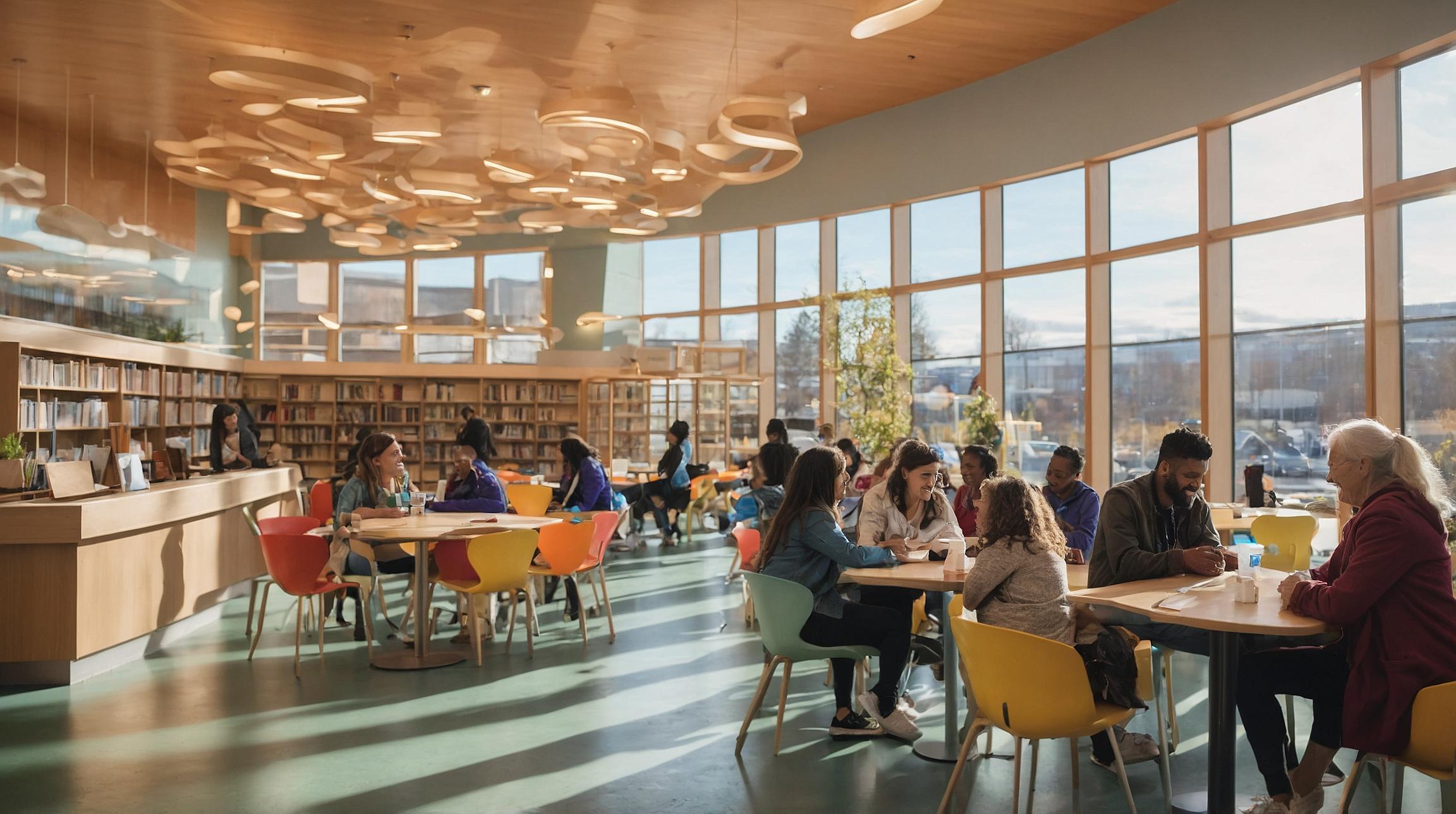
While much focus is on physical infrastructure, the ‘social infrastructure gap’ is often overlooked. This gap includes public spaces such as parks, cafes, libraries, community centres, and museums, which are essential for fostering social connections and community cohesion.
Challenges Facing Social Infrastructure
In recent years, social infrastructure has faced significant challenges:
- UK local council funding cuts have led to almost 800 library closures and strained budgets for local museums and parks.
- Over 7,000 pubs have closed in the last decade.
- A record one in seven UK shops are empty, signifying the troubling decline of the high street.
Impact on Communities
Social infrastructure serves as a foundation for creating social bonds, which is essential for thriving communities. During the Covid-19 pandemic, community aid groups played a crucial role in delivering vital support and helping to combat loneliness and mental illness.
Economic and Social Benefits
The decline in social infrastructure can lead to:
- Increased loneliness and mental health issues that strain healthcare resources.
- Higher crime rates and anti-social behavior, diverting public resources and deterring investment.
Investing in social infrastructure has clear economic benefits:
- Every £1 million invested could return £1.2 million in fiscal savings and £2 million in economic and social benefits.
Importance to Democracy
Social infrastructure is vital for democracy as it allows grassroots political movements to emerge. Public spaces enable people with different views to meet and build common understanding, which is missing in our tech-driven world.
Steps to Rebuild Social Infrastructure
Improving Data Quality:
- Better metrics are needed to measure social capital and social infrastructure to fully grasp the problem.
Convincing Decision-Makers:
- Policymakers need to understand how social infrastructure fits into economic and political agendas.
Responsibility for Maintenance:
- There needs to be a balance between private management and community ownership of public spaces.
- Targeted Policies:
- Areas with depleted social infrastructure, often the same areas facing economic decline, must be prioritized.
Conclusion
When planning for the future, governments must recognize the importance of social infrastructure. Investments in these areas create stronger, more connected communities, boost economic productivity, and support democratic vitality. Prioritizing the repair and growth of these public spaces is essential for a better future.